EXPLORE the Laurisilva of Madeira with this slideshow, check the location map and get all the facts and information below.
For slideshow description see right or scroll down (mobile). Click to view slideshow
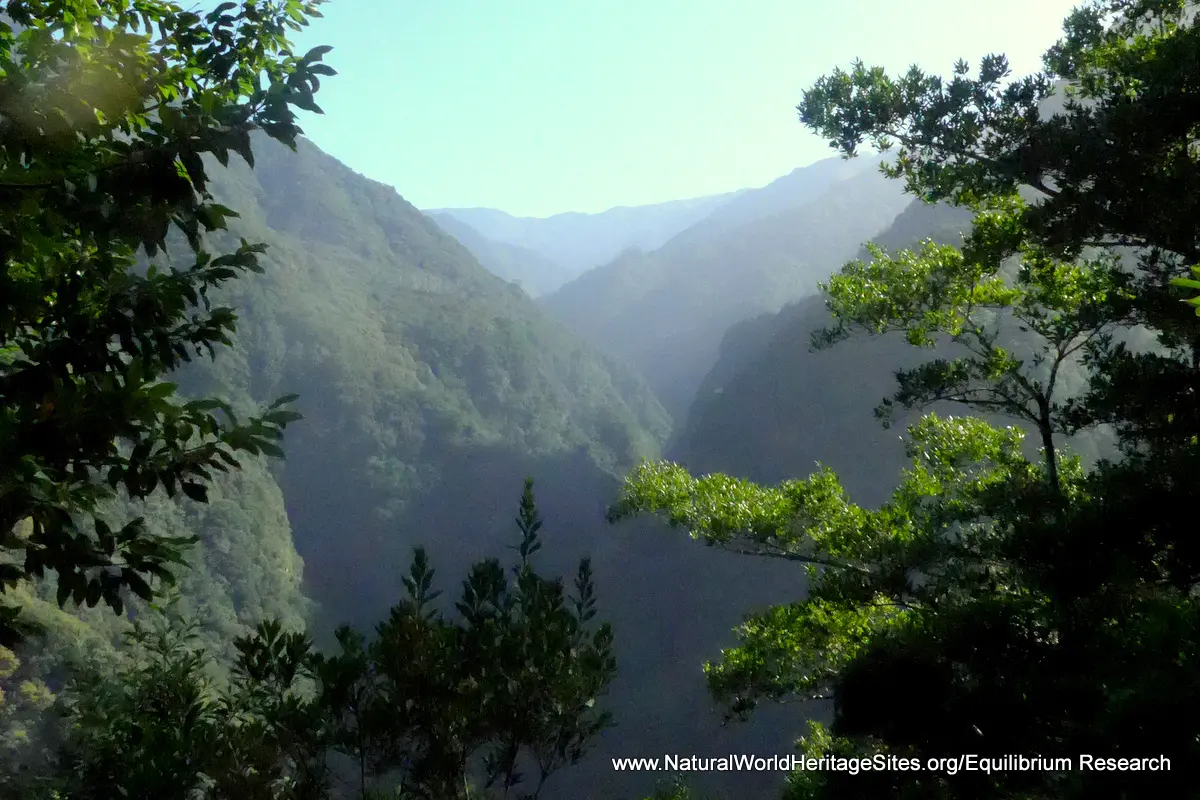
Location and Values: The Laurisilva of Madeira is located on the Portuguese island of Madeira, in the eastern Atlantic Ocean, about 1,000 km from the European coast and 400km north of the Canary Islands. The area designated as world heritage represents about 20% of the island’s total land area, and serves to protect one of the largest surviving tracts of laurel forest. This vegetation type covered much of southern Europe 15-40 million years ago but is now confined to the Azores, Madeira and the Canary Islands (where it is also protected within Garajoney National Park, another world heritage site). The Laurisilva is important for biodiversity conservation with at least 76 plant species endemic to Madeira, including four dominant trees from the Lauraceae family (commonly known as the Barbusano, Laurel, Til and Vinhatico). More than 500 species of invertebrate animals (insects, spiders and mollusks) are also known to be endemic to the Laurisilva, together with a limited number of vertebrate species (notably two birds – the Madeira Laurel Pigeon and Madeiran Firecrest, and the Madeiran Pipistrelle bat)
Conservation Status and Prospects. According to IUCN’s Conservation Outlook Assessment (2017) the conservation status of the Laurisilva of Madeira is of ‘significant concern’. The IUCN report notes a number of threats to the integrity of the site, including the spread of invasive alien species; the impacts of climate change; an increase in the incidence of wild fires; pressures from tourism and inadequate resources for effective management. Nevertheless, despite these concerns, the report notes that the site’s World Heritage values have so far been mostly preserved and remain stable.
Links:
Google Earth
UNESCO Official Website
IUCN Conservation Outlook
UNEP-WCMC Site Description
Birdlife IBA
Slideshow description
The slideshow ‘tells the story’ of the Laurisilva of Madeira with a portfolio of photos by Sue Stolton (Equilibrium Research) from a visit in February 2017. They illustrate the landscape features of this outstanding place, together with some of the typical plants and animals (including the endemic Laurel Pigeon). The settlers of Madeira constructed water channels, known as levadas, through the forest to provide for the domestic and irrigation needs of local villages, and paths alongside these channels provide easy access into the site. Remarkably, the trees have never been cut and 90% of the primary forest remains, with some massive old trees possibly over 800 years old. The Laurisilva covers the steep northern slopes of the island from its highest elevations right down to the coast so the range of forest types and coastal scenes are illustrated. Also shown are some features of the wider landscape outside the site (where forestry, livestock grazing and small-scale crop production are the predominant forms of commercial land use).
Factfile
Website Categories: Temperate & Boreal Forests;
Area: 150 km2
Inscribed: 1999
Criteria:
- Ecological processes (ix);
- Significant number of rare, endemic and/or endangered species (x)