EXPLORE the Hubei Shennongjia with this slideshow, check the location map and get all the facts and information below.
For slideshow description see right or scroll down (mobile). Click to view slideshow
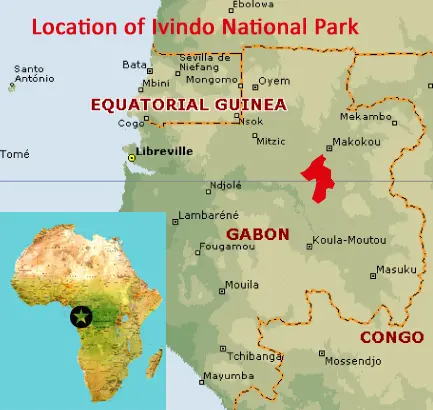
Location and Values: Ivindo National Park is located in the heart of the Lower Guinea forests of central Gabon, where the Ivindo and Djidji rivers trace their courses through virgin forest in a series of spectacular waterfalls and stretches of deep, calm black waters. The park is home to an extraordinary diversity of habitats and species, including many rare and endangered plants, mammals, birds and fish, with many species not yet described. The forest includes large areas of very old Caesalpinioideae forests, monodominant Julbernardia forests and a diversity of other forest types, many of which are unique to the Lower Guinea region.
Swampy forest clearings (Bais) provide occasional open habitats where large mammals – gorillas, forest elephants, forest buffalo and sitatunga – congregate, while other threatened species – such as chimpanzees, mandrills, grey parrot, rockfowl, pangolins, leopards and golden cats – may prefer the cover of the forest. An indication of the extraordinary biodiversity of this largely unexplored area is provided by the discovery in the black waters of the Ivindo River of a swarm of some fifteen species of fish of the genus Paramormyrops (Mormyridae) – the only swarm of species from this family found in rivers worldwide. It is one of the world’s best examples of speciation in open waters.
Conservation Status and Prospects. According to IUCN’s Conservation Outlook Assessment (2025) the conservation status of the Ivindo National Park is ‘good with some concerns’. The IUCN report considers the site to be well protected and in a stable, pristine condition, largely due to its large size and remote location. However there is a lack of available ecological monitoring data, as well as reliable information on park finances, management and protection activities.
There are some concerns over management of the site including the need for an updated Management Plan which takes into account the needs of local communities and the impacts of the logging concessions which surround most of the park. Forest elephants are a ‘keystone species’ of particular concern as they have been subject to historic poaching which may have resulted in a decline of ‘big tuskers’. There is ongoing human-elephant conflict to the north of the park, which may be exacerbated by habitat disturbance, road construction and selective logging in forestry concessions in other areas around the park. Increased monitoring is needed to assess the threats of illegal killing of elephants and the risk of Ebola and other diseases which could quickly decimate the population of great apes.
Another potential threat is the development of an iron ore project (outside the park at Belinga) as this would bring increased human population pressure around the park and require the construction and operation of a railway to transport the iron ore, as well as other infrastructure.
LINKS:
Slideshow description
Slideshow Description: The slideshow features a short portfolio of photographs showing some of the magnificent waterfalls, bais and iconic wildlife species of the area, including forest elephants, western lowland gorillas, the (critically endangered) slender-snouted crocodile and two of the unique species of mormyrid fish.
The following Flickr photographers and other sources are acknowledged with thanks for their contributions to this slideshow: amazinggabon.com; wildsafariguide.com; Joost van Veen; Cornell University; Carlos Reis; Alex Echtermeyer and Jefe Le Gran (see watermarks in each photo for details).
Factfile
Website Category:
Tropical and sub-tropical forests;
Area: 2,988 km2
Inscribed: 2021
Criteria:
- Ecological processes (ix);
- Natural habitat for biodiversity (x);
- Significant number of rare, endemic and/or endangered species (x)